How do interest rates and inflation affect forex?

What is ‘the interest rate’?
The interest rate is the overall lending rate in a country, which ties into the overall rate worldwide. A country’s interest rate is either the stipulated amount at which commercial banks borrow from one another, or the rate at which commercial banks may borrow from the central bank.
The most important interest rate is set by a central bank like the Federal Reserve (Fed), which affects all other interest rates in an economy. Central banks of very influential economies such as the United States, the UK and China will affect developing countries’ rates too.
If the rate is hiked, the increased cost of borrowing by banks is passed onto businesses and consumers who then pay increased interest rates on loans, which also constrains spending. If the interest rate is reduced, loans become cheaper to pay back and spending increases.
The interest rate is used as a tool to help control inflation and stimulate economic growth during periods of stagnation.
How do interest rates affect exchange rates?
Interest rates affect the exchange value in the forex market because the rates’ movements directly impact demand for a currency.
This is because interest rates are a measure of the rate of return on certain investments and savings. Due to the relative attractiveness of the interest rate, investors may want to move capital into or out of a country, which impacts the supply and demand for a specific currency.
However, it’s important to remember that the effect of interest rate changes on forex is never guaranteed. It also doesn’t happen in isolation, but rather depends on several factors such as the perception of an economy’s future strength and stability.
As exchange rates depend on the supply and demand of a particular currency, all factors that impact on either of these will affect the value of the currency. You should have this top of mind at all times when you conduct analyses of the markets.
Learn more about how forex works
The demand for forex when interest rates increase
When interest rates are increased, you can achieve a better rate of return on savings deposits, lending or government and corporate bonds.
In theory, money will move from currencies in economies with less desirable investment opportunities to a currency with better prospects, positively impacting its exchange rate. The flow of money will drive demand up for the preferable currency, while the currencies experiencing less demand will depreciate. This will, in turn, negatively affect the exchange rate.
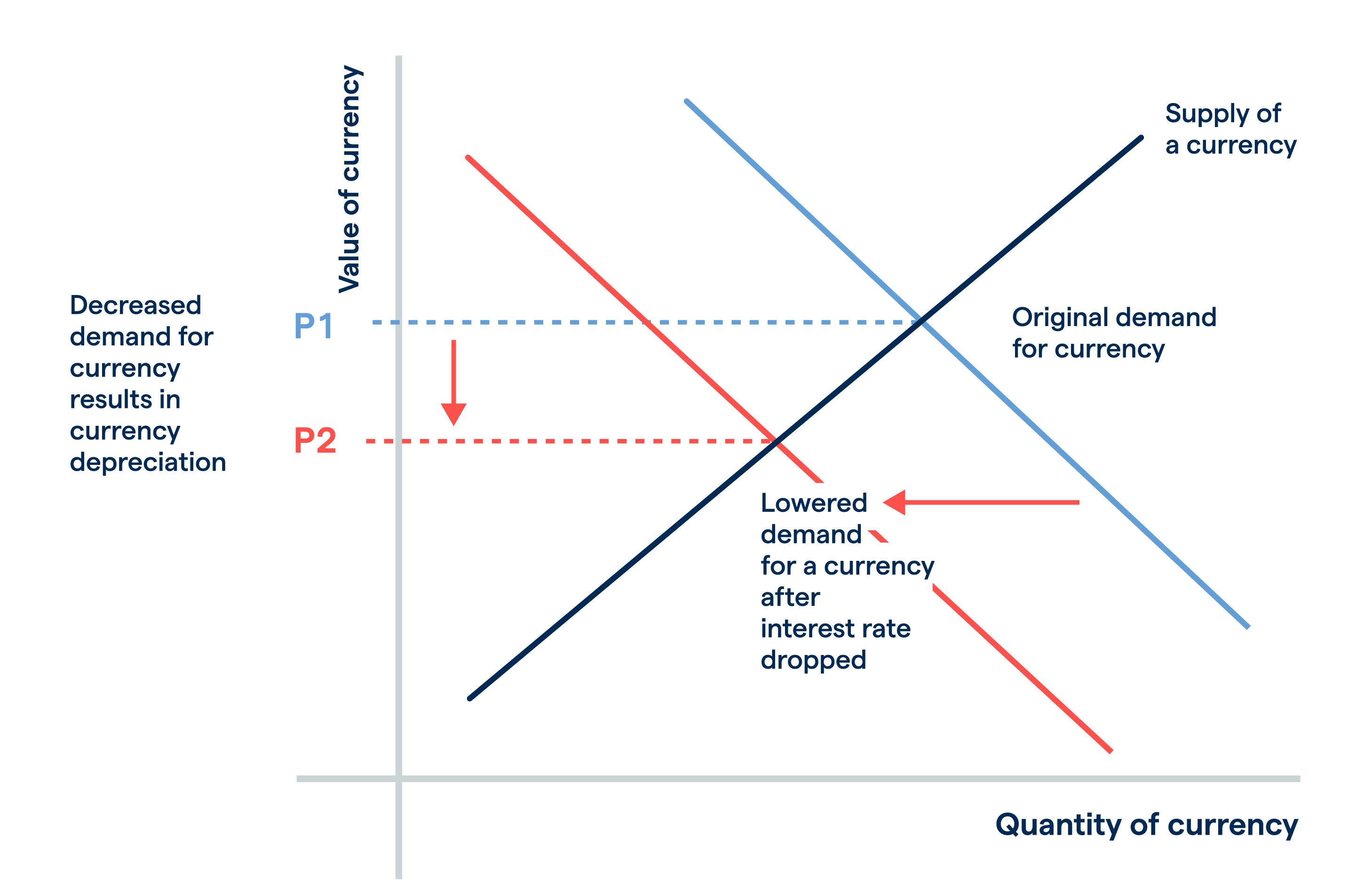
The demand for forex when interest rates decrease
When interest rates decrease, investors can expect a lower rate of return on savings deposits, lending or government and corporate bonds.
Again, theoretically, investors may find better opportunities elsewhere. This means the demand for that currency will fall, due to the fact that investment capital flows are diverted to more attractive investment destinations. This would depress that country’s exchange rate. It would also increase the supply of the domestic currency in forex markets and drive the price of the currency down further.
What is inflation?
Inflation is the rate of increase in the cost of goods and services in an economy. The adjustment to inflation impacts the spending power of consumers, which has a spiralling effect on business’ ability to produce goods due to the spike in the cost of raw materials.
Inversely, when the price of goods and service decrease substantially, and the value of the currency strengthens, this effect is referred to as deflation. The central bank of the country is responsible for adjusting the level of inflation and uses the consumer price index (CPI) to measure the rate.
How does inflation affect exchange rates?
When inflation is high, the value of a country’s currency weakens. This is because goods become more expensive, and it becomes less attractive for investors to do business. The inverse is also true. When there’s significant lowering of inflation, there tends to be more flow of money in a country, the buying power of the currency becomes more valuable, and the exchange rate strengthens.
Why inflation causes interest rate hikes
The central bank raises interest rates to slow down economic activity because people have more money to spend. The inflation rate would have to be low for a country to experience a hike in interest rates. Low inflation stimulates movement of money, and an increase in interest rates encourages people to spend less.
What’s ‘balance of trade’ and how does it affect forex?
Balance of trade is the variance between a country’s income due to exports and its expenditure due to imports. Balance of trade can further be broken down into balance of trades for goods or for services.
When inflation drives up the price of goods and services within an economy, that nation becomes less competitive in the international marketplace, resulting in exporters losing ground to cheaper countries. This means that the ‘balance of trade’ is altered and demand for the currency declines. This in turn will affect the foreign exchange rate.
During times of high inflation, foreign goods and services become more attractive to consumers and businesses as they’re cheaper. This means that imports will increase. Consequently, this causes an increase in the currency supply in forex markets which results in a depreciated currency.
How to trade forex markets
To start trading forex:
- Research your preferred market
- Create a live account or practice on a demo
- Click ‘buy’ to go long or ‘sell’ to go short
- Take steps to manage your risk
- Open and monitor your trade
When trading with leverage, you’ll need to pay an initial deposit called margin to open a position and increase your exposure to your foreign exchange currency of your choice. While leverage can magnify your profits, it’ll amplify your losses and possibly exceed your initial account size.
With us, you can trade the US dollar by choosing a forex pair that includes the American currency. Forex trading involves buying one currency while selling another based on how much each currency is valued on the FX market.
For instance, the current market price of the GBP/USD forex pair shows how many US dollars it would take to buy one pound. Some of the other common forex pairs you can trade are the USD/CAD, USD/CHF, USD/JPY and AUD/USD.
How do interest rates and inflation affect forex summed up
- Interest rates are the predetermined amounts by which banks may borrow from the central bank or each other
- Interest rates can affect exchange rates and cause volatility in forex markets, which may be seen as an opportunity for traders
- Inflation, the rate at which prices in the economy are rising, also affects the forex market
- You can trade forex with us using a live or demo account in the spot market
This information has been prepared by tastyfx, a trading name of tastyfx LLC. This material does not contain a record of our trading prices, or an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument. You should not treat any opinion expressed in this material as a specific inducement to make any investment or follow any strategy, but only as an expression of opinion. This material does not consider your investment objectives, financial situation or needs and is not intended as recommendations appropriate for you. No representation or warranty is given as to the accuracy or completeness of the above information. tastyfx accepts no responsibility for any use that may be made of these comments and for any consequences that result. See our Summary Conflicts Policy, available on our website.
