How to Pick a Position Size in Forex Trading
Learn effective forex position sizing strategies to manage risk, protect your capital, and maximize potential gains.
What is a position size in forex trading?
Position size in financial markets refers to the quantity of a particular asset or security that is bought or sold in a trade. It is a crucial element of any trading strategy, directly influencing both the potential risk and reward of the trade in question, as well as the broader portfolio. By determining position size, traders can control their exposure to market movements and decide how much capital they are willing to risk on a given trade. Position size is usually calculated based on the trader's risk tolerance, the amount of capital in their account, and the level of volatility in the market. Properly managing position size helps ensure that traders are not overexposed to any single trade, helping to protect their capital.
In the context of forex trading, position size becomes even more important due to the unique dynamics of the currency market. Forex traders often deal with higher volatility and leverage, which can magnify both profits and losses. Unlike futures, spot forex offers greater position sizing flexibility - dealers like tastyfx allow trades as small as 0.01 lots (requiring only about $22 margin for EUR/USD) that can scale incrementally up to 1000+ lots. The position size determines how much of a currency pair is being bought or sold, which in turn dictates how the trader's account balance will be affected by a given move in price. With leverage, remember that your position can control up to 50x your required margin, meaning price fluctuations can impact your account beyond your initial investment. Traders typically calculate their position size by determining how much of their account they are willing to risk on a single trade, usually as a percentage of their total capital. This method helps to maintain a balanced risk-reward ratio, and is intended to help ensure that no single trade has a disproportionate impact on the trader's overall portfolio.
Position size is closely linked with risk management, and the tools used to help mitigate risk. For example, a stop-loss order is a predetermined point at which a trade will be automatically closed to limit potential losses. By setting appropriate position sizes in conjunction with stop-loss levels, forex traders can control their overall risk exposure, ensuring they don't lose more than they are comfortable with on a single trade. Understanding position size is not only key to managing risk, but also for helping to use leverage effectively. In the highly leveraged forex market, a trader's ability to calculate the appropriate position size therefore helps ensure that they can take advantage of opportunities without exposing themselves to excessive risk.
Importance of position sizing in forex
Position sizing is one of the most important aspects of risk management in forex trading. It refers to how much of a currency pair a trader buys or sells in a given trade, and directly affects the trader's exposure to market risk. Proper position sizing can help traders manage how much they are willing to lose on a trade, while also ensuring they can maximize their potential gains. Without a clear strategy for determining position size, traders can easily overexpose themselves, risking too much capital on a single trade, which can lead to significant losses.
In the highly volatile forex market, where price fluctuations can be sharp and rapid, position sizing allows traders to maintain control over their trades. By calculating position size based on their account balance and risk tolerance, traders can set stop-loss levels that protect their capital, even in the event of an unexpected market move. Stop-loss orders are critical for defining your precise risk, as forex trades are inherently unlimited risk without them, unlike options or defined-risk strategies. This helps ensure that the losses associated with a single position do not have a devastating impact on their overall portfolio. For instance, a trader may decide to risk 1-2% of their total capital on each trade, allowing them to endure several losing trades without significantly affecting their account balance.
Moreover, position sizing plays a vital role in taking advantage of leverage in forex trading. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with less capital, but it also amplifies both potential profits and risks. By properly calculating position size in relation to the leverage they are using, traders can strike a balance between maximizing profit opportunities and minimizing excessive exposure to risk. In short, position sizing is critical not just for preserving capital but also for ensuring a disciplined and strategic approach to trading in the forex market. It is a cornerstone of the risk management process, helping traders make calculated decisions that align with their outlook and goals.
How to pick a position size
Picking the right position size is a crucial component of any successful forex trading strategy. Position size determines how much capital you're committing to a trade and plays a key role in managing risk. By calculating the appropriate position size, traders can control their exposure to market fluctuations, protect their capital, and align with their broader trading goals. A well-defined position sizing strategy helps traders avoid overexposure to any single trade, ensuring that they don't risk too much of their account balance on one position.
To pick the right position size, it can help to follow a structured process, and one that aligns with the trader's strategic approach, outlook, and risk profile. For example, traders can consider the following steps when choosing position size: select the currency pair, determine your market outlook, decide on the amount of risk you're willing to take, set a stop-loss level, calculate your position size, and adjust for leverage. Each of these steps contributes to finding a balanced position size that aligns with your risk tolerance and trading objectives.
Below, these steps are outlined in greater detail:
- Select a currency pair: The first step in determining position size is choosing the currency pair you want to trade. Different pairs have different volatility, and some pairs may require different position sizes to manage risk effectively. For instance, a currency pair with higher volatility (like GBP/USD) may require a smaller position size to keep risk in check, while a less volatile pair (like EUR/USD) may allow for a larger position size. Also be aware that each currency pair requires a different amount of margin, usually 2-5%.
- Determine your market outlook: Your position size should also reflect your outlook on the currency pair. If you have a strong conviction that a trend will continue in your favor, you may choose a larger position size, assuming it aligns with your risk tolerance. On the other hand, if the market outlook is uncertain or you're trading based on shorter-term fluctuations, you might choose a smaller position size.
- Decide how much risk you want to take: One of the most important steps in position sizing is determining how much of your account you are willing to risk on a single trade. Most traders risk a small percentage of their total capital—typically between 1% and 3%—on each trade. For example, if you have a $10,000 account and decide to risk 2% on a trade, your total risk per trade would be $200.
- Set a stop-loss order: After finalizing your position size, you may elect to deploy a stop-loss order. A stop-loss is a predetermined point at which you'll exit the trade if the market moves against you. The distance between your entry price and the stop-loss level may influence your position size. For example, if you expect more market volatility, you might select a wider stop-loss, which might involve a smaller position size.
- Calculate the position size: To calculate the appropriate position size, you need to understand the relationship between your risk amount, stop-loss distance, and the pip value for your specific currency pair and account currency. For standard forex lots (100,000 units), a typical formula would be:
- Position Size in Lots = Risk Amount/(Stop-Loss in Pips × Pip Value per Standard Lot). For example, if you're risking $200 on EUR/USD with a 50-pip stop-loss, and 1 pip on a standard lot equals $10, your position size would be: Position Size = $200/(50 × $10) = 0.4 standard lots.
- Remember to adjust the pip value based on your specific currency pair and account currency, as these values vary. The tastyfx platform calculates pip values automatically in the trade ticket to help you determine appropriate position sizing.
- Adjust for leverage: The next step is to consider the leverage you are using in your trade. Leverage allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, and the amount of leverage varies for every currency pair. It's important to remember that while leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses - so calculate your position size while accounting for leverage, ensuring that your exposure doesn't exceed your comfort level or risk tolerance.
Position size example
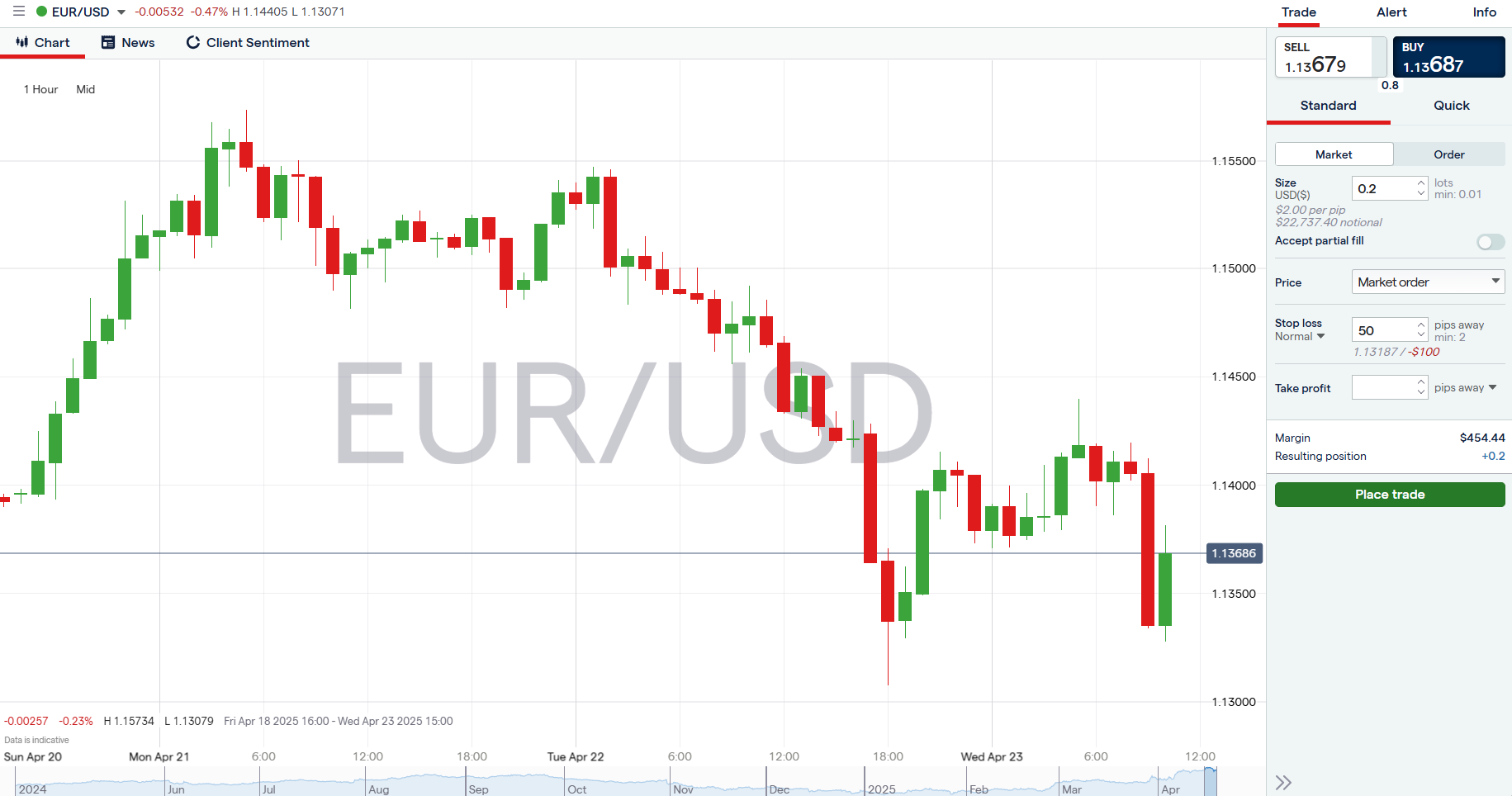
Now let's consider a hypothetical example using the EUR/USD currency pair, one of the most commonly traded pairs in the forex market. The steps outlined below can help traders calculate position size, depending on their trading approach, outlook, and risk profile.
- Select the currency pair: For this hypothetical example, we'll use EUR/USD (Euro to U.S. Dollar). This is a popular pair with lower spreads, high liquidity, and relatively lower volatility compared to some other pairs.
- Determine your market outlook: Imagine you have a bullish outlook on the Euro and expect EUR/USD to rise due to strong forthcoming economic data from the Eurozone. Based on this outlook, you decide to take a long position (buy) on EUR/USD.
- Decide on your risk percentage: For this hypothetical example, let's assume you're willing to risk 1% of your $10,000 account balance on this trade. This means you're willing to risk $100 per trade.
- Consider setting a stop-loss order: In this hypothetical example, you enter a position at 1.1375 and place your stop-loss at 1.1325, which is 50 pips away from your trade entry point. The stop-loss distance is important because it will influence your position size.
- Calculate the value of 1 Pip for EUR/USD: For EUR/USD, the value of 1 pip is typically $10 for a standard lot (100,000 units). However, since we are calculating a smaller position, the pip value will adjust accordingly for smaller lot sizes.
- Calculate the position size: Now, use the above information in this formula: Position Size = Risk Amount/(Stop-Loss in Pips × Value of 1 Pip). Your risk amount is $100, the stop-loss is 50 pips, and the pip value for a standard lot (100,000 units) is $10. Plugging these values into the formula: Position Size = 100/(50 × 10). That means the position size is equal to 20,0000 or 0.2 standard lots.
- Consider adjusting for leverage: EUR/USD gives you 50:1 leverage, so you would only need ~$454 in margin to control the 20,000 units. However, it's important to keep in mind that using leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses, so you should always ensure you're not overexposed relative to your risk tolerance.
Forex trading position sizing key takeaways
- Position size determines how much of a currency pair you buy or sell, influencing both potential profits and losses.
- Position size is critical for risk management, as it directly impacts the amount of capital you risk on a single trade.
- Selecting the right position size requires balancing factors like risk tolerance, stop-loss levels, and market volatility.
- Traders typically risk a small percentage of their account (usually 1-3%) on each trade to avoid overexposure, and to preserve/protect capital.
- Key steps in calculating position size include choosing the currency pair, determining your market outlook, deciding on risk, setting a stop-loss, calculating position size, and adjusting for leverage.
- Leverage amplifies both potential profits and risks, so understanding position size in conjunction with leverage is essential to avoiding excessive exposure.
- Stop-loss orders can be essential tools in position sizing—they can help limit losses and protect capital if the market moves against you. It's important to remember that stop-losses do not guarantee fills at the specified price, since they become market orders once triggered.
- By calculating position size properly, traders can help ensure they're not risking too much on a single trade, while still deploying their best ideas in the market.
- Effective position sizing can help maintain discipline in trading, preventing impulsive decisions.
- By adjusting position size based on market conditions and risk tolerance, traders can help themselves achieve the optimal outcome, not only from a reward standpoint, but from a risk standpoint.
