What is the spread in forex and how do you calculate it?

What is a spread in forex?
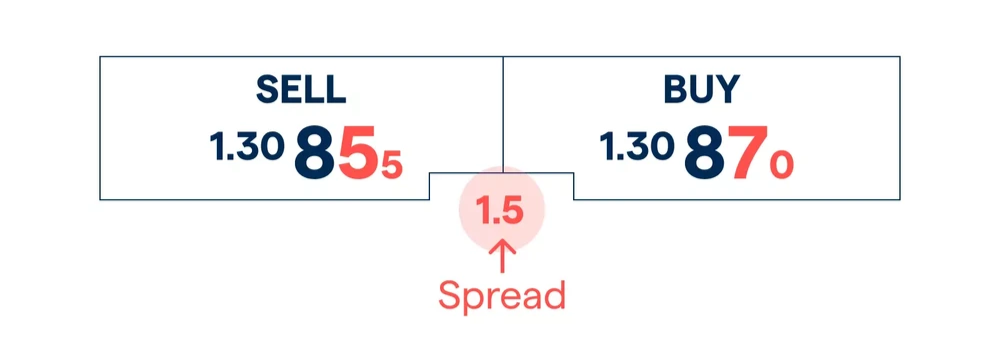
The spread in in forex is a small cost built into the buy (bid) and sell (ask) price of every currency pair trade. When you look at the price that’s quoted for a currency pair, you will see there is a difference between the buy and sell prices—this is the spread or the bid/ask spread.
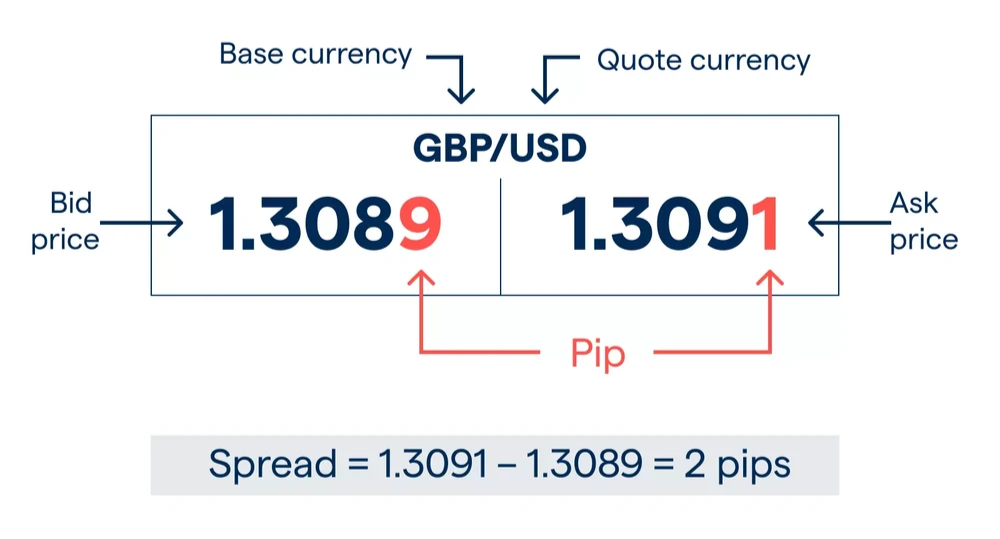
Changes in the spread are measured by small price movements called pips – which is any change in the fourth decimal place of a currency pair (or second decimal place when trading pairs quoted in JPY). It is not only the spread that will determine the total cost of your trade, but also the lot size. Remember, every forex trade involves buying one currency pair and selling another. The currency on the left is called the base currency, and the one on the right is called the quote currency. When trading forex, the bid price is the cost of buying the base currency, while the ask price is the cost of selling it.
With us, you’ll be trading forex using leverage. This enables you to get exposure to large amounts of currency without having to pay the full value of their trade upfront. You can go long or short, which means you can speculate on rising as well as falling currency prices. And, you only need a small deposit—called margin—to open your position.
The margin can be as low as 2% of the value of the trade, which means you can make your capital go further while still getting exposure to the full value of the trade. Note, margin will magnify both your profits and your losses.
Learn more about our costs and charges
How to calculate spread in forex
To calculate the spread in forex, you have to work out the difference between the buy and the sell price in pips. You do this by subtracting the bid price from the ask price. For example, if you’re trading GBP/USD at 1.3089/1.3091, the spread is calculated as 1.3091 – 1.3089, which is 0.0002 (2 pips).
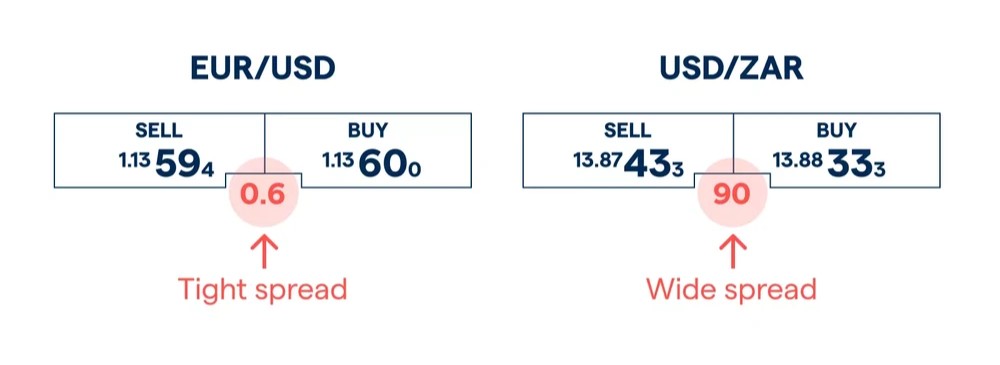
Spreads can either be wide (high) or tight (low) – the more pips derived from the above calculation, the wider the spread. Traders often favor tighter spreads, because it means the trade is more affordable.
If the forex market is very volatile and not very liquid, spreads will likely be wide, and vice versa. For example, major currency pairs such as EUR/USD will have a tighter spread than an emerging market currency pair such as USD/ZAR. However, spreads can change, depending on the factors explained next.
How are currencies quoted?
Currencies are quoted in pairs, which indicate the value of one currency relative to another. This pair format is essential in forex trading, where one currency is bought and the other is sold simultaneously. Here's how currency pairs are structured:
- Base and Quote Currency: The exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For instance, if EUR/USD is quoted at 1.1500, it means 1 euro is equivalent to 1.1500 US dollars.
- Exchange Rate: The exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For instance, if EUR/USD is quoted at 1.1500, it means 1 euro is equivalent to 1.1500 US dollars.
- Direct vs. Indirect Quotation: Direct quotation is when the domestic currency is the quote currency (e.g., USD/JPY for an American trader). Indirect quotation is when the domestic currency is the base currency (e.g., JPY/USD for a Japanese trader).
- Bid and Ask Price: Bid price is the price at which the market (or your broker) will buy the base currency. You can sell the base currency at this price. The ask price is the price at which the market (or your broker) will sell the base currency. You can buy the base currency at this price. The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the "spread."
- Pip: A pip is the smallest price movement that can be observed in a currency pair. Most currency pairs are quoted to four decimal places (e.g., EUR/USD 1.1501), so a pip is 0.0001. For pairs involving the Japanese yen, a pip is typically 0.01.
Understanding these components is crucial for forex traders, as they form the basis for quoting, trading, and analyzing currency pairs in the market.
How are forex spreads quoted?
Forex spreads are the difference between the bid and ask prices of a currency pair and can be expressed in pips. Here's a table illustrating how forex spreads are typically quoted:
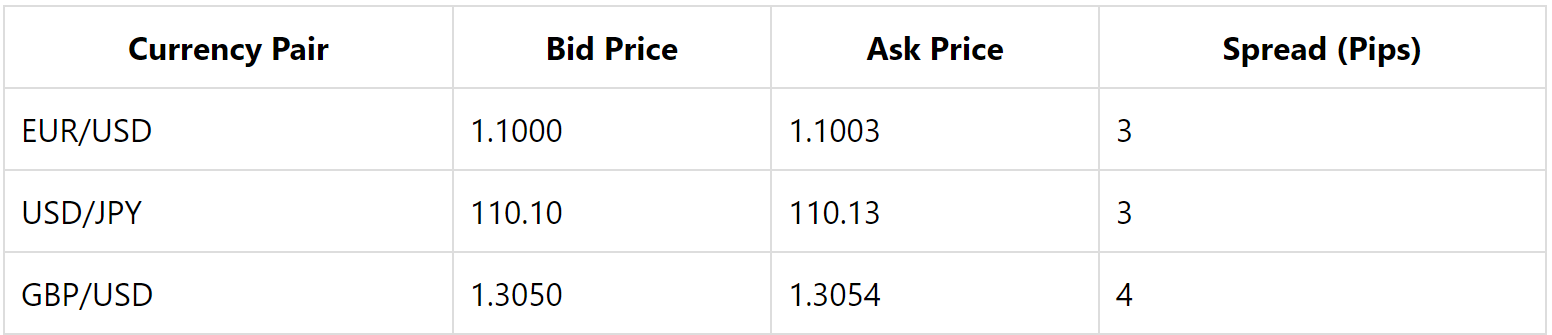
This table shows typical spreads for some major currency pairs. The spread represents the broker's compensation for facilitating the trade and can vary based on market conditions, volatility, and forex broker policies.
Why does the spread change in forex?
The spread in forex changes when the difference between the buy and sell price of a currency pair changes. A forex pair’s spread may increase if there is an important news announcement or an event that causes higher market volatility. One of the downsides of a variable spread is that, if the spread widens dramatically, your positions could be closed, or you’ll be put on margin call. Keep an eye on our economic calendar to stay abreast of upcoming financial events.
Market Liquidity:
During times of high market liquidity, such as when major financial centers like London and New York are open, spreads tend to be narrower. More buyers and sellers are active, increasing the ease of matching trades. In contrast, during off-peak hours or when markets are closed for holidays, liquidity drops, leading to wider spreads. Fewer market participants make it harder to find a matching counterparty.
Market Volatility:
Increased volatility, often due to economic news releases (like GDP reports, employment data, or central bank announcements), can lead to wider spreads. Rapid price movements create uncertainty, and brokers widen spreads to manage the risk of executing trades at unfavorable prices. Geopolitical events or sudden market shocks can also increase volatility, affecting spreads.
Economic Indicators:
Key economic data releases from major economies can impact spreads. For instance, a surprise change in the US non-farm payrolls or Eurozone inflation statistics might cause market fluctuations, prompting brokers to adjust spreads.
Broker Policies:
Different brokers have different business models. Some offer fixed spreads, which remain constant under normal market conditions, while others offer variable spreads, which fluctuate based on market dynamics. Brokers may adjust spreads to reflect changes in market conditions, aiming to optimize their own risk management.
Currency Pair Characteristics:
Major currency pairs, like EUR/USD or GBP/USD, generally have tighter spreads because they are traded more frequently and have higher liquidity. Exotic currency pairs might have wider spreads due to lower liquidity and higher volatility.
Interest Rates and Monetary Policy:
Central bank policies and interest rate changes can influence forex spreads. For example, a central bank raising rates can attract foreign capital, affecting currency demand, market liquidity, and in turn, spreads.
Global Economic Conditions:
Broader economic trends, such as trade tensions, pandemics, or financial crises, can affect foreign exchange markets globally. During economic uncertainty, spreads may widen as market conditions become less predictable. By understanding these factors, forex traders can better anticipate changes in spreads, allowing them to adjust their strategies and risk management practices to ensure more effective trading.
What type of forex spreads are there?
In forex trading, spreads come in two types: fixed and variable.
Fixed Spreads: stay constant, offering predictability and stability, which is useful during volatile markets. However, they tend to be higher than variable spreads and can lead to re-quotes in fast markets.
Variable Spreads: fluctuate with market conditions, potentially offering lower costs and transparency during stable markets. They can widen unpredictably during volatility, increasing trading costs and risk.
When choosing between them, traders who value stable costs might prefer fixed spreads, while those trading in high liquidity might opt for variable spreads. The choice depends on trading strategy and risk tolerance.
Forex spread trading strategies
Trading forex spreads involves understanding the dynamics of bid and ask prices and implementing strategies that capitalize on spread movements. Here are some popular strategies for trading spreads effectively:
Scalping:
Scalping involves making multiple trades over a short period to capitalize on small price movements. Traders aim to profit from small spreads by entering and exiting positions quickly. Scalping functions best in highly liquid markets with tight spreads, such as during major market sessions like London or New York.
News Trading:
This strategy involves trading around major economic news releases, which can cause increased volatility and wider spreads. Traders attempt to capture the initial movement or the subsequent reversal. It requires close monitoring of economic calendars and quick decision-making to manage potential risks from spread widening.
Range Trading:
Traders identify well-defined support and resistance levels to trade within a range. Profits are made as prices move back and forth within these levels. It works best in stable markets where spreads are predictable and not affected by sudden news events.
Carry Trade:
Involves borrowing in a currency with a low-interest rate and investing in one with a higher rate. Traders earn the interest rate differential, which can offset spread costs. It is important to maintain awareness of interest rate changes and market volatility, which can affect profitability.
Breakout Trading:
Focuses on capturing profits from a currency pair breaking out of a defined range or pattern, often after a period of consolidation. It is important to look for tight spreads during low volatility periods and trade the breakout as spreads might widen. Set stop-loss points to mitigate risk.
Event-Driven Strategy:
This strategy involves trading based on specific events, such as elections or central bank meetings, which can influence currency movements and spreads. Spreads can widen significantly, so it requires precise timing and risk management.
Swing Trading:
A medium-term strategy where traders hold positions for several days or weeks, aiming to profit from expected swings in the market. Swing trading it less affected by spread fluctuations since trades are held longer, focusing more on directional movements.
Each strategy requires a good understanding of market conditions and appropriate risk management practices. The choice of strategy should align with the trader’s goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Traders should consider using stop-loss orders and keep abreast of market news to adjust strategies as needed.
What is a good forex spread?
A good forex spread is typically tight, meaning the difference between the bid and ask prices is small. For major currency pairs like EUR/USD, a spread of 1-3 pips is generally considered good.
What is a one pip spread?
A 1 pip spread means the difference between the bid and ask price is 1 pip. In most currency pairs, this is the smallest price change, typically 0.0001. So, if EUR/USD has a bid of 1.1000 and an ask of 1.1001, the spread is 1 pip.
Why do forex spreads widen at 10 pm?
Forex spreads often widen at 10pm because major market centers are closed, leading to lower liquidity and less trading activity. This reduced liquidity makes it harder to match buyers and sellers, prompting brokers to widen spreads to manage risk.
This information has been prepared by tastyfx, a trading name of tastyfx LLC. This material does not contain a record of our trading prices, or an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument. You should not treat any opinion expressed in this material as a specific inducement to make any investment or follow any strategy, but only as an expression of opinion. This material does not consider your investment objectives, financial situation or needs and is not intended as recommendations appropriate for you. No representation or warranty is given as to the accuracy or completeness of the above information. tastyfx accepts no responsibility for any use that may be made of these comments and for any consequences that result. See our Summary Conflicts Policy, available on our website.
